String in Python
In this tutorial, you will learn about strings in Python with its other methods and functions.
- Introduction to strings in Python
- Multiline Strings
- Accessing Characters in a String
- Length of a String
- Concatenate Strings
- Looping Through a String
- Get Substring from a String
- Formatting Strings
- Best Practices
- Conclusion
Table Of Contents
Introduction to Python String
A String is a sequence of characters used to store text data. It is the most used data type in Python.
The string is created by enclosing characters inside a single (' ') or double quote (" "). For example: 'Hello World' or "Hello World".
Python strings are immutable, which means that once created, they cannot be changed.
Declaring and initializing a string
To declare a string in Python, you can use either single or double quotes. It can be assigned to a variable.
# Single quotes
string1 = 'Hello, World!'
print(string1)
# Double quotes
string2 = "Hello, World!"
print(string2)Hello, World! Hello, World!
Common Uses
Strings can be used in many ways. Some of the common uses are:
- Storing text data
- Storing HTML code or other long text
- Ouputting text to the user
- Reading text from the user
- Reading text from a file
Multiline Strings
Strings are not necessarily limited to a single line. We can have a string that spans multiple lines.
But you can't use single or double quotes to span multiple lines. This will result in an error.
string = 'This is a # ❌ EOL (End of Line)
multiline string'
print(string)To span multiple lines in Python use triple quotes (' ' ' or " " ").
Anything written between triple quotes will be considered as a string.
string1 = '''This is a
multiline string'''
print(string1)
# or
string2 = """This is a
multiline string"""
print(string2)This is a multiline string This is a multiline string
Note: Triple quote is also used for declaring multi-line comments in Python.
Accessing Characters in a String
You can think of a string as a list of characters, where each character has an index.
The index of the first character is 0, the second character is 1, and so on.
For example, the string 'Hello, World!' has 13 characters. The first character is 'H' (index = 0) and the last character is '!' (index = 12).
str = 'Hello, World!'
# 1st character
print(str[0]) # H
# 2nd character
print(str[1]) # e
# last character
print(str[len(str) - 1]) # !H e !
You can also access the string from the end using the negative index. The last character is at index -1, the second last character is at index -2, and so on.
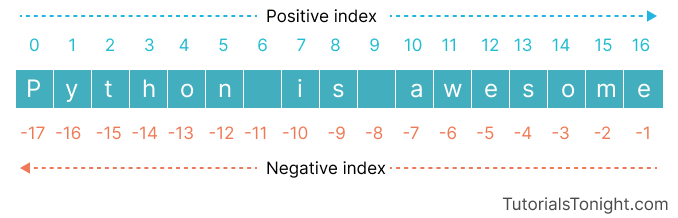
str = 'Hello, World!'
# last character
print(str[-1]) # !
# second last character
print(str[-2]) # d! d
Length of a String
To get the length of a string in python, use the built-in len() function.
It returns the number of characters in a string.
str = 'Hello, World!'
# length of string
print(len(str)) # 1313
Concatenating Strings
While working with strings we often need to concatenate them. Concatenation is the process of joining two or more strings together.
There are two ways to concatenate strings in Python.
- Using + operator
- Using join() method
Using + Operator
Using + operator is the simplest way to concatenate strings in Python.
It joins two strings together and returns a new string.
str1 = 'Hello'
str2 = 'World'
# concatenate strings
str3 = str1 + str2
print(str3) # HelloWorldHelloWorld
You can also concatenate multiple strings together.
str1 = 'Hello'
str2 = 'World'
str3 = '!'
# concatenate strings
str4 = str1 + " " + str2 + str3
print(str4) # Hello World!Hello World!
Using join() Method
The join() is a method that returns a new string by concatenating all the elements of a given iterable (list, tuple, string etc.) separated by a string separator.
str1 = 'Hello'
str2 = 'World'
# concatenate strings
str3 = ' '.join([str1, str2]) # join with space
print(str3) # Hello WorldHello World
Looping Through a String
As mentioned earlier, you can imagine a string as a list of characters. Therefore, you can loop through the string, character by character just like you would loop through a list.
Here is an example to loop through a string using for loop.
str = 'Hello'
# loop through the string
for char in str:
print(char)H e l l o
Get Substring from a String
A substring is a part of a string. You can get a substring from a string by slicing it.
To slice a string, you need to specify the start and end index, separated by a colon : inside square brackets [].
str = 'Hello, World!'
# get substring
substr = str[1:5]
print(substr) # elloello
If you omit the start index, the slice will start from the beginning of the string.
Learn more about slicing in Python.
String Formatting
String formatting in Python is used to insert variables into strings.
There are several ways to format strings in Python.
- Using the % operator
- Using the format() method
- Using the f-string method
name = 'Mark'
age = 25
# using % operator
print('My name is %s and I am %d years old.' % (name, age))
# My name is Mark and I am 25 years old.
# using format() method
print('My name is {} and I am {} years old.'.format(name, age))
# My name is Mark and I am 25 years old.
# using f-string
print(f'My name is {name} and I am {age} years old.')
# My name is Mark and I am 25 years old.My name is Mark and I am 25 years old. My name is Mark and I am 25 years old. My name is Mark and I am 25 years old.
To learn string formatting in detail, read String Formatting in Python.
Best Practices
Here are some best practices to follow when working with strings in Python.
- Be consistent with quotes in your program.
- Using single quotes can make it easier to include a double quote character within the string, and vice versa.
- Use string formatting to insert variables into strings, rather than concatenating them.
- Use the triple-quote syntax (single or double) to define multi-line strings.
Quiz - Python string tutorial quiz
s?What is the result of the following code?
string = "Hello, World!"
print(string[2:5])What is the result of the following code?
string = "Hello, World!"
print(string[-5:-2])Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned about strings in Python and how to use them in a program. We covered topics such as string concatenation, slicing, formatting, and more.
Thank you for following along with this tutorial. We hope you have a better understanding of Python strings and how to use them in your code.
Happy coding!🙂
