What is the Internet?
The Internet changed the world in every possible way, be it social, political, economic, or technological. It has made the world a smaller place by bringing people together from all over the world. It has made the world a global village.
Nowadays, it is hard to imagine a world without the Internet. It has become an integral part of our lives. It has changed the way we communicate, the way we shop, the way we learn, the way we play, the way we work, even the way we think.
We are so dependent on the Internet that we can't even imagine our lives without it.
For people before the Internet, it would be like magic to be able to communicate or share information with someone on the other side of the world. But now, it is just a matter of seconds.
In this article, you will learn about the Internet, its history, how it works, and anything and everything about it.

- Define Internet
- History of Internet
- How does the Internet Work?
- Internet Protocols
- Internet Services and Applications
- Internet vs World Wide Web
- Conclusion
Table of Contents
Define Internet
The Internet is a global network of billions of computers and other electronic devices connected to each other through a common protocol called Internet Protocol (IP).
The Internet is a network of networks connecting billions of computers worldwide, allowing them to send and receive data from each other.
It carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as electronic mail, online chat, file transfer, and the interlinked web pages and other documents of the World Wide Web.
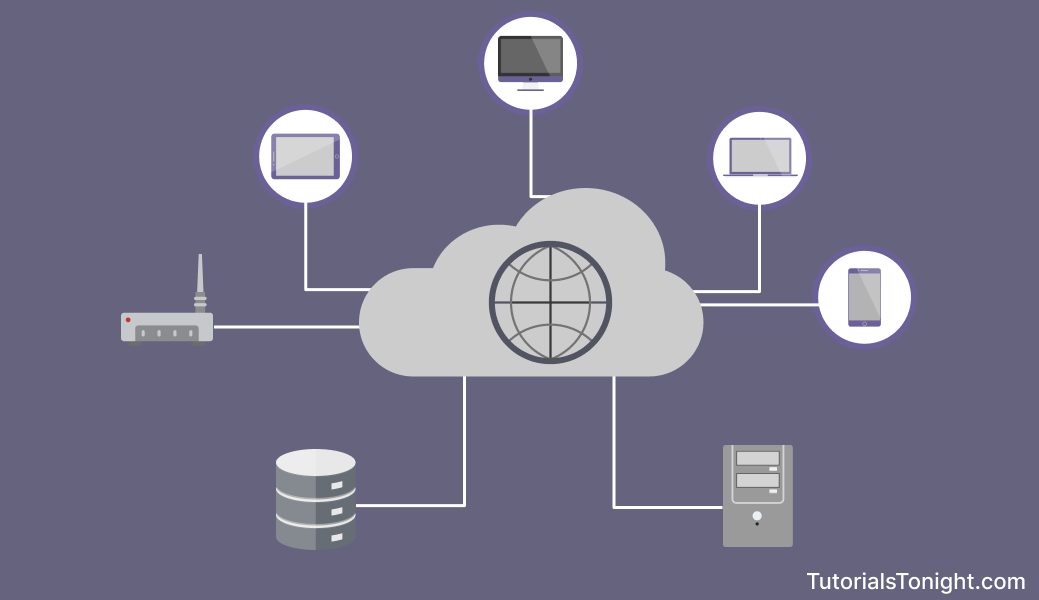
Let's understand the concept of the Internet in simple terms.
Let there be 2 computers, A and B, and connect them with a cable. These two computers can now send, receive, and request data from each other. Suppose A has a file that B wants to access, then A can send that file to B through this cable and vice-versa.

Similarly, you can connect 3, 4, 5, or any number of computers with each other and they can share data with each other.
We have created a small network of computers. Internet is a network of such networks, but it uses many different ways to connect computers with each other like optical fiber, radio waves, satellite, etc.
Each computer on the Internet has its own unique address, just like houses on a street have different house numbers. This address helps the computers find each other and know where to send or receive information.
In simple terms, the Internet is like a big digital neighborhood where computers chat, share, and collaborate, making the world a much smaller and more connected place.
History of Internet
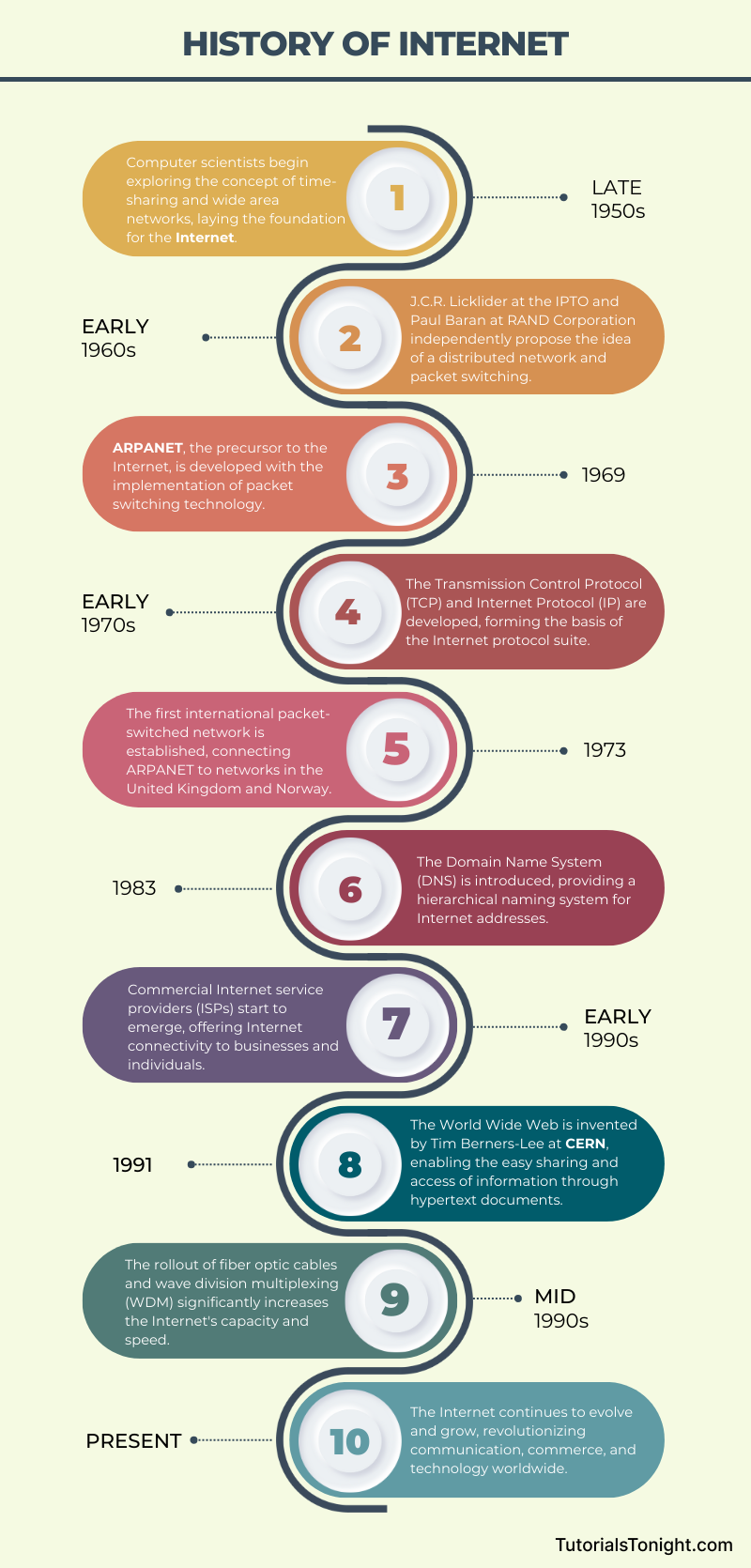
The Internet is a relatively new technology. It was invented in the late 1960s, but it wasn't until the early 1990s that it became popular.
In 1983, ARPANET adopted TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) as its standard. TCP/IP is a set of rules that governs how data is transmitted over the Internet.
The Internet was originally developed by the United States Department of Defense to connect their computers and share information with each other.
The first computer network was created in 1969 by the United States Department of Defense. It was called ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network).
It was a huge success and soon other countries started to develop their own networks. In 1983, ARPANET adopted TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) as its standard.
By the late 1980s, ARPANET was replaced by NSFNET (National Science Foundation Network). It was a network of networks that connected academic users together.
The World Wide Web (WWW) was invented in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee. It was a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet.
By the early 1990s, the Internet was opened to the public and it became popular. In 1995, NSFNET was decommissioned and the Internet became a commercial network.
Since then, the Internet has grown exponentially and has become an integral part of our lives.
How does the Internet Work?
Working of the Internet is a very complex process. It involves many different devices, technologies, and protocols at different levels.
We will try to understand the workings of the Internet in simple terms.
- Devices and Networks - The Internet involves various devices such as computers, smartphones, servers, routers, and more. These devices are connected to each other through different types of networks, including wired and wireless connections. Internet service providers (ISPs) provide the infrastructure and connectivity for users to access the Internet.
- IP Address - Every device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique identifier called an IP (Internet Protocol) address. IP addresses are similar to phone numbers or street addresses and allow devices to send and receive data packets across the Internet.
- Data Packet Transmission - When you send or receive information over the Internet, it is broken down into smaller units called data packets. Each data packet contains a portion of the data being transmitted, as well as addressing information (source and destination IP addresses) that helps in routing the packets to their intended destination.
- Routing - Routers are responsible for directing data packets across the Internet. They examine the destination IP address in each packet and determine the most efficient path to transmit the packet towards its destination. Routers communicate with each other to exchange information about network topology and determine the best routes.
- Protocols - Protocols are a set of rules and standards that govern how data is transmitted and received over the Internet. The most fundamental protocol is the Internet Protocol (IP), which handles addressing and routing of packets. Some of the most common protocols used on the Internet are TCP/IP, HTTP, FTP, SMTP, POP, IMAP, and more.
Internet Protocols
Internet Protocol is a set of rules that determines how data is transmitted over the Internet. It is the foundation of the Internet and allows devices to communicate with each other.
It provides addressing and routing information that helps in transmitting data packets across the Internet.
The most common Internet protocols are TCP/IP, HTTP, FTP, SMTP, POP, IMAP, and more.
- TCP/IP - Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is the most widely used Internet protocol. It consists of two protocols: TCP and IP. TCP is responsible for breaking down data into packets and reassembling them at the destination. IP is responsible for addressing and routing of packets.
- HTTP - Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) allows web browsers to communicate with web servers.
- FTP - File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a protocol that allows users to transfer files between computers. It is used to upload and download files from a remote server.
- SMTP - To send and receive emails, we use Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
- POP - Post Office Protocol (POP) is a protocol that allows users to retrieve emails from a remote server. It downloads emails from a remote server to a local computer.
- IMAP - Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) is a protocol that allows users to access emails stored on a remote server. It is used to access emails from a remote server without downloading them to a local computer.
Internet Services and Applications
Applications and services are what makes the Internet so useful. If we start listing all the applications and services that are available on the Internet, it will take forever. So, we will only discuss the most popular ones.
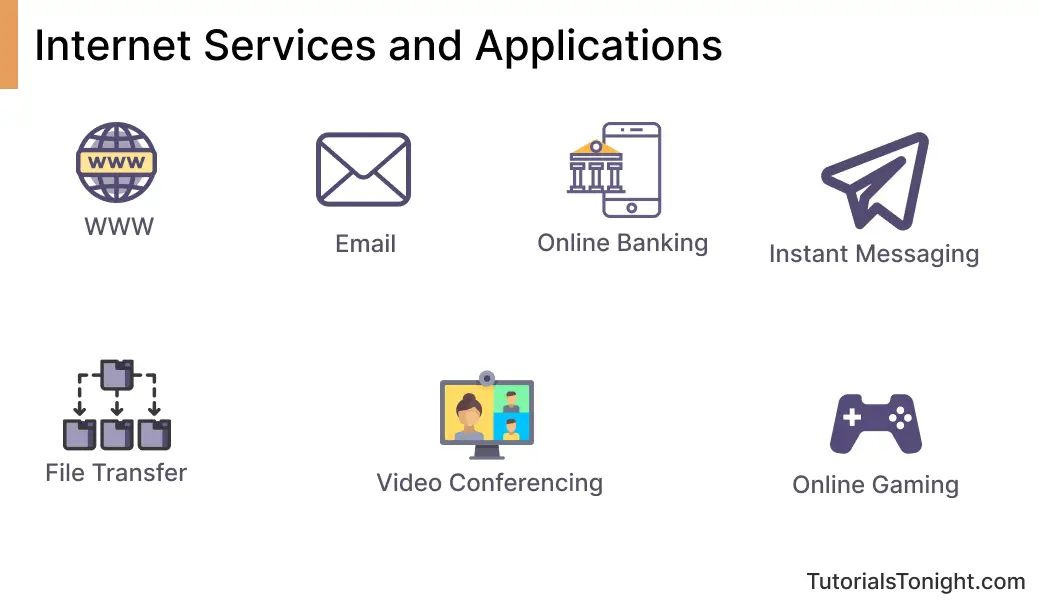
- World Wide Web (WWW) - It is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet. It is the most popular service on the Internet and allows users to access and interact with information on the web.
- Email - Email is a service that allows users to send and receive messages over the Internet. It is one of the most popular services on the Internet and is used by millions of people every day.
- Instant Messaging - Instant messaging is a service that allows users to send and receive messages in real time over the Internet. Services like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, Telegram, etc. are very popular.
- File Transfer - Whenever you post a photo on Facebook, upload a video on YouTube or download a movie, you are using a file transfer service. It allows users to transfer files between computers over the Internet.
- Online Gaming - Gaming is one of the most popular activities on the Internet. There are thousands of online games available on the Internet that allow users to play with each other in real-time.
- Video Conferencing - Video conferencing is a service that allows users to communicate with each other in real-time using video and audio. Services like Zoom, Google Meet, Skype, etc. are very popular.
- Online Banking - Due to the Internet, we can now do banking from the comfort of our homes. We can transfer money, pay bills, check account balance, etc. without visiting the bank.
Internet vs World Wide Web
The Internet and the World Wide Web (WWW) are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same thing.
The Internet is the underlying infrastructure that enables global connectivity and communication between devices, while the World Wide Web is a collection of interconnected documents and resources accessible via the Internet.
In simple terms, the Internet is the network, and the World Wide Web is a service or application that runs on top of that network.
| Internet | World Wide Web | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A global network connecting devices worldwide. | A collection of interconnected web pages and resources accessible via the Internet. |
| Infrastructure | Physical network of interconnected devices. | Virtual space consisting of websites and web pages. |
| Connectivity | Enables devices to connect and communicate with each other. | Provides access to websites and online content. |
| Protocols | TCP/IP, DNS, HTTP, FTP, etc. | HTTP, FTP, SMTP, POP, IMAP, etc. |
| Purpose | Facilitates data transmission and communication across networks. | Allows users to access and interact with information on the web. |
Conclusion
The Internet is a platform that connects billions of computers, sharing information and resources with each other. We are so dependent on the Internet that if the Internet stops working for a day, it will cause a huge loss to the world economy.
The Internet has been evolving evolving since its birth and it will continue to evolve in the future. Every day, new technologies are being developed to make the Internet faster, more secure, and more reliable.
You will be surprised to know that only 5% of the internet is visible to the public. The rest 95% is hidden in the deep web and dark web. The deep web is the part of the internet that is not indexed by search engines like Google, Bing, etc. and can only be accessed through special technologies and softwares.
