Javascript Date Format
In this article, we are going to learn how to format Javascript date in a human readable format. We will create a few methods and also look at some predefined methods like toLocaleDateString().
- Introduction
- Custom Methods To Format Date
- Built-in Methods To Format Date
- Date and time in local language and country
- Local time string
- Custom date format to pass to date object
Table Of Contents
1. Introduction to Javascript Date Format
The Date object gives us the current date and time in Javascript. But the date object returned is not in the form we write or see in our day-to-day life.
Example
let date = new Date();
console.log(date);The key information like date, month, year, hours, and minutes need to be extracted from the date object.
We need to manually convert the date to the format we read or write. Like dd/mm/yyyy, dd-mm-yyyy, etc.
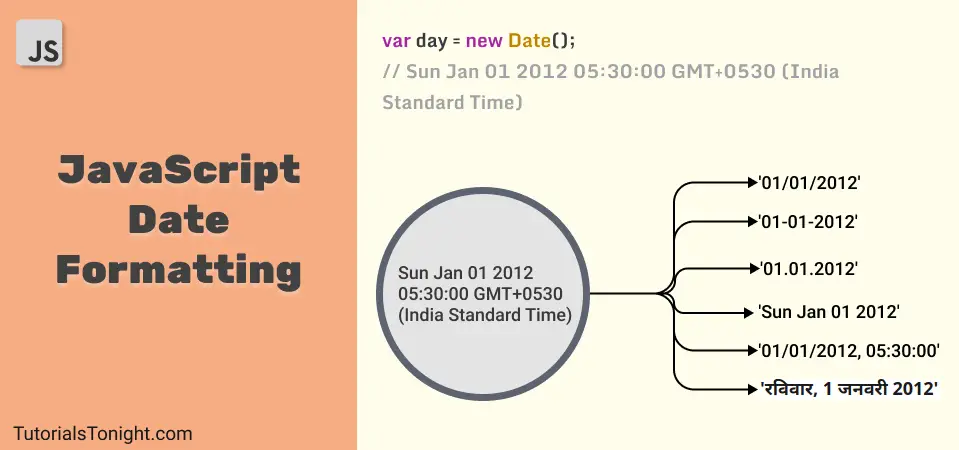
In this tutorial, you will learn different ways to convert the standard date format into the format shown in the above image, and the process of this conversion is known as date formatting in Javascript.
2. Custom Methods To Format Javascript Date
Let's create our own method to convert the date object into the format we need.
The date that we see written anywhere in our day to day life are in the following format:
- dd/mm/yyyy
- dd-mm-yyyy
- yyyy-mm-dd
- dd.mm.yyyy
- monthdd, yyyy
We will create a function that will take a date object and return the date in the format we need.
2.1. Date Formatting function
To format the date in the order mentioned above, we have to first get a date, month, and year from the date object and then order the date in the format mentioned above within the function.
Example
// format date javascript
function dateFormater(date, separator) {
var day = date.getDate();
// add +1 to month because getMonth() returns month from 0 to 11
var month = date.getMonth() + 1;
var year = date.getFullYear();
// show date and month in two digits
// if month is less than 10, add a 0 before it
if (day < 10) {
day = '0' + day;
}
if (month < 10) {
month = '0' + month;
}
// now we have day, month and year
// use the separator to join them
return day + separator + month + separator + year;
}
var now = new Date();
console.log(dateFormater(now, '/'));
console.log(dateFormater(now, '-'));
console.log(dateFormater(now, '.'));Function code explanation:
- Take a date object and a separator as arguments.
- Get the date, month, and year from the date object and store them in variables.
- For a better look add an extra 0 to the date and month if they are less than 10.
- Finally, join the date, month, and year using the separator and return it.
2.2 Javascript date format dd-mm-yyyy
The date format we need here is dd-mm-yyyy. To format the date in this format, we can use the above function and pass the separator as - (dash).
The code below will show how to format the date in this format.
Example
var date = new Date();
// format date javascript
function dateFormater(date, separator) {
var day = date.getDate();
// add +1 to month because getMonth() returns month from 0 to 11
var month = date.getMonth() + 1;
var year = date.getFullYear();
// show date and month in two digits
// if month is less than 10, add a 0 before it
if (day < 10) {
day = '0' + day;
}
if (month < 10) {
month = '0' + month;
}
// now we have day, month and year
// use the separator to join them
return day + separator + month + separator + year;
}
console.log("dd-mm-yyyy => " + dateFormater(date, '-'));There is also a built-in method in javascript to format the date in this format. It is toLocaleDateString().
Look at the example below:
Example
var date = new Date();
console.log("dd-mm-yyyy => " + date.toLocaleDateString());2.3. Javascript format date yyyy-mm-dd
To format date as yyyy-mm-dd we need to just rearrange the returning value of the dateFormater() function.
The overall function will be the same but in this, we rearrange the returning value in which year comes first then the month, and then the date.
Example
// format date javascript
function dateFormater(date, separator) {
var day = date.getDate();
var month = date.getMonth() + 1;
var year = date.getFullYear();
// show date and month in two digits
if (day < 10) {
day = '0' + day;
}
if (month < 10) {
month = '0' + month;
}
// now we have day, month and year
// use the separator to join them
return year + separator + month + separator + day;
}
var now = new Date();
console.log('yyyy-mm-dd => ' + dateFormater(now, '-'));2.4. Format Date month dd, yyyy
An example of monthdd, yyyy format could be January01, 2020.
In this format we need to show the name of the months, so we will create an array that stores the names of the months and when we get the month number from the date object, we will use the array to get the name of the month.
Example
function dateFormater(date) {
var months = ['Jan', 'Feb', 'Mar', 'Apr', 'May', 'Jun', 'Jul', 'Aug', 'Sep', 'Oct', 'Nov', 'Dec'];
var day = date.getDate();
// get month from 0 to 11
var month = date.getMonth();
// conver month digit to month name
month = months[month];
var year = date.getFullYear();
// show date in two digits
if (day < 10) {
day = '0' + day;
}
// now we have day, month and year
// arrange them in the format we want
return month + ' ' + day + ', ' + year;
}
console.log(dateFormater(new Date()));3. Using Built-in Methods
JavaScript has some built-in methods to format the date. We can use them to format the date.
In this section, we will look at all the useful methods that can help you to format the date.
List of javascript methods that help us to format the date:
- Date.toDateString() - returns the date in the format day mth dd yyyy.
- Date.toTimeString() - returns the time in the format hours:minutes:seconds timezone.
- Date.toLocaleDateString() - returns the date in the format dd/mm/yyyy.
- Date.toLocaleTimeString() - returns the time in the format hh:mm:ss tt.
- Date.toLocaleString() - returns the date and time in the format dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:ss.
- Date.toUTCString() - returns the date and time in the format day, dd month yyyy hh:mm:ss GMT.
- Date.toISOString() - returns the date and time in the format yyyy-mm-ddThh:mm:ss.sssZ.
- Date.toJSON() - returns the date and time in the format yyyy-mm-ddThh:mm:ss.sssZ.
- Date.toString() - returns the date and time in the format day month dd yyyy hh:mm:ss GMT.
Example
var now = new Date();
console.log(now.toDateString());
console.log(now.toTimeString());
console.log(now.toLocaleDateString());
console.log(now.toLocaleTimeString());
console.log(now.toLocaleString());
console.log(now.toUTCString());
console.log(now.toISOString());
console.log(now.toJSON());
console.log(now.toString());4. Date And Time In Local Language And Country
The toLocaleDateString() method can be used to get a formatted date in the local language and country.
The toLocaleDateString() method takes two arguments, the first one is the language code and the second one is the format of the date.
Syntax:
date.toLocaleDateString(languageCode, format)The language code could be:
en-US- Sunday, January 1, 2012hi-IN- रविवार, 1 जनवरी 2012es-ES- domingo, 1 de enero de 2012fr-FR- dimanche 1 janvier 2012de-DE- Sonntag, 1. Januar 2012ja-JP- 2012年1月1日日曜日ko-KR- 2012년 1월 1일 일요일zh-CN- 2012年1月1日星期日- etc.
The format of date is an object that has 5 properties: weekday (long, short, narrow), year (numeric), month (long, short, narrow), day (numeric), and timezone (UTC, etc.).
Example of date object is { weekday: 'long', year: 'numeric', month: 'long', day: 'numeric', timeZone: 'UTC' } where all the informations are optional and can be used in any combination.
Example
var date = new Date();
var options = {
weekday: 'long',
year: 'numeric',
month: 'long',
day: 'numeric',
timeZone: 'UTC'
};
console.log(date.toLocaleDateString('en-US', options));
console.log(date.toLocaleDateString('hi-IN', options));
console.log(date.toLocaleDateString('es-ES', options));
console.log(date.toLocaleDateString('fr-FR', options));
console.log(date.toLocaleDateString('de-DE', options));Here is another example with the different combinations of options.
Example
var date = new Date();
console.log(date.toLocaleDateString('en-US', { weekday: 'short', year: 'numeric', month: 'long', day: 'numeric' }));
console.log(date.toLocaleDateString('en-US', { year: 'numeric', month: 'short', day: 'numeric' }));
console.log(date.toLocaleDateString('en-US', { weekday: 'long', year: 'numeric', month: 'long' }));
console.log(date.toLocaleDateString('en-US', { weekday: 'long', year: 'numeric' }));5. Local time string
The toLocaleTimeString() method returns a formatted string time in the local language and country.
The toLocaleTimeString() method takes language code as an argument.
Syntax:
date.toLocaleTimeString(languageCode)Here is an example:
Example
var date = new Date();
console.log(date.toLocaleTimeString('en-US'));
console.log(date.toLocaleTimeString('hi-IN'));
console.log(date.toLocaleTimeString('ko-KR'));6. Custom date format by passing date string
The new Date() returns the current date and time in the local time zone, but you can also pass in a string to create a date object of any specific date and time.
Syntax:
new Date(dateString)Suppose our date string be 'January 25, 2000 23:15:30' then we can create a date object by passing this string to the new Date() method.
Example
var date = new Date('January 25, 2000 23:15:30');
console.log(date.toString());6.1 JavaScript Short Date String
Only Year:
Example
var date = new Date('2000');
console.log(date.toString());Only Year and Month:
Example
var date = new Date('2000-01');
console.log(date.toString());Year, Month and Day dash separated:
Example
var date = new Date('2000-01-25');
console.log(date.toString());Year, Month, and day slash separated:
Example
var date = new Date('2000/01/25');
console.log(date.toString());dd/mm/yyyy format (Invalid Date)
Example
// invalid date format
var date = new Date('25/01/2000');
console.log(date.toString());6.2. JavaScript Long Date String
Year, Month, Day, Hour, Minute, Second and Millisecond:
Example
var date = new Date('2000-01-25 23:15:30.500');
console.log(date.toString());Month name, date, year
Example
var date = new Date('January 25, 2000');
console.log(date.toString());
// case insensitive
date = new Date('JANUARY 25, 2000');
console.log(date.toString());Conclusion
We have discussed both the built method and the custom method to format javascript date in this article. You can use any of them to format the date.
With little modification in the custom method, you can also create another format for your use.
