Data Types In JavaScript
In this tutorial, you will learn about what is a data type, different data types in JavaScript, and how to use them in your code.
Javascript Data Types
Data type is a type of data that can be stored in a variable. Example:
var myVar1 = "Hello World"; // String
var myVar2 = 1; // Number
var myVar3 = true; // BooleanmyVar1 is of type string myVar2 is of type number myVar3 is of type boolean
Javascript is a dynamically typed language means variable data type is defined by language itself. We don't need to explicitly mention the data type of the variable.
You can think of it as putting different types of fruits in the same container. You need not have different containers for different types of fruits. You can put any type of fruit in the same container.
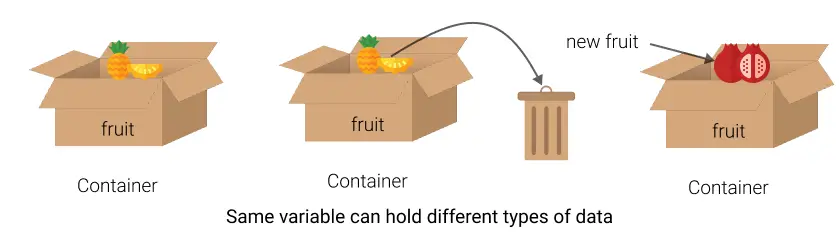
// Dynamically Typed
var x = 10; // can store a number
x = "javascript"; // now x is a String
x = true; // now x is a booleanTypes of Data in JavaScript
There are two types of data in JavaScript:
- Primitive data type
- Non-primitive data type
Primitive Data Type
Primitive data types are the data in javascript that are not objects, like numbers, strings, etc. These data types have no methods.
There are seven primitive data types in javascript:
- Number
- String
- Boolean
- BigInt
- Undefined
- Null
- Symbol
Non-primitive Data Type
Objects are non-primitive data types in JavaScript. Objects are data that have methods and properties.
Other data types are called primitive because they can only hold one type of data but non-primitive data types can hold different types of data as a collection.
Examples of non-primitive data types in JavaScript are array, object, function, date, etc.
JavaScript Data Types
Look at the table below for a brief description of each data type.
| Data Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Number | Number are integers and floating point numbers | 10, -10, 10.5, -10.5, etc |
| String | String are sequences of characters | 'Hello World', "Hello World", '10', "10", etc |
| Boolean | Boolean are true or false | true, false |
| BigInt | BigInt is a number that is bigger than 2^53 - 1 | 961719254740951n, -961719254740951n, etc |
| Null | Null is a value that is not defined | null |
| Undefined | Undefined is a special value that is used to represent the absence of a value | undefined |
| Symbol | Symbol is a unique and immutable data type that is used to represent unique values | Symbol(foo) |
| Object | Object is a collection of properties and methods | var car = {name: "fiat"} |
Let's now discuss all the data types in JavaScript in detail.
Number
The Number is a primitive data type that represents integer, float, exponential, hexadecimal, octal, and binary numbers. It can be created using number constructor.
Numbers can be written in exponential and in decimal form in javascript. Example 1, 2, -3, 0, 23.3, 45.02, 12e2, 10e-1 etc.
Example
var int_type = 10; // Integer
var float_type = 15.55; //Float
var exponential_type = 12.2e2; // exponential 12.2e2 = 1220
var hexadecimal_type = 0x15f; // hexadecimal 0x15f = 351
var octal_type = 020; // octal 020(octal) = 16 (decimal)
console.log(int_type);
console.log(float_type);
console.log(exponential_type);
console.log(hexadecimal_type);
console.log(octal_type);String
String is a series of characters in javascript. Example "Hello World", "10", "10.5", etc.
Anything between single or double quotes is a string. String is immutable means it cannot be changed after it is created.
Example
let lang = 'javascript'; // using single quote
let greet = "Welcome!"; // using double quote
console.log(lang, greet);Boolean
Boolean is a data type that represents true or false values. It is used for yes-no, on-off purposes.
Example
let x = true;
let y = false;
console.log(x, y);BigInt
BigInt represents whole numbers that are bigger than 2^53 - 1.
It is created by using BigInt() constructor or by appending n to the end of the integer. Example: 961719254740951n.
Example
let bigInt = 961719254740951n;
console.log(bigInt);Null
Null is a special value that is used to represent the absence of a value.
null is different from undefined. null is nor equal to '' (empty string) neither equal to 0. null means there is nothing.
Undefined
Undefined is a special value that is used to represent the absence of a value.
When a variable is defined and not assigned any value then it is undefined.
Example
let a; // currently undefined
console.log(a);
a = 10; // now defined a = 10
console.log(a);Symbol
Symbol is a special data type that is used to represent a unique and immutable name. It is created using Symbol() constructor.
symbols are unique every time it is invoked.
Object
Object is a special data type that is used to represent a collection of properties. It is created using Object() constructor.
It is a non-primitive data type that holds data in the form of key-value pairs. It stores collections of different types of data.
The property key is always a string, but the value could have any data type.
Here is a simple example to show how to create objects and use them.
Example
var student = {
"name": "clark", // value string
"age": 21 // value number
};
console.log(student);
console.log(student.name, student.age);Array
Array is a special data type that is used to represent a collection of values. It is created using Array() constructor.
Array is a non-primitive data type that is used to store multiple values in a single variable which is accessed through index value. Each value stored in the array has a position value that starts with 0, known as the index of the array.
To get array value we write name_of_array[position]. So if the name is arr, then the first value will be arr[0], the second value will be arr[1], and so on.
Example
var fruits = ['Mango', 'Banana', 'Orange', 'Guava'];
console.log(fruits);
console.log(fruits[0]);
console.log(fruits[3]);Function
Function is a special data type that is used to represent a block of code that is not bound to a variable. It is created using Function() constructor.
The function can be used for some action multiple times. In javascript, the function can be assigned to some variable.
Example
var myFunction = function() { // Defining function
console.log("function called"); // block of code
};
myFunction(); // calling functiontypeof operator
typeof operator in javascript is an operator which is used to find data type of any variable. To get the data type of variable "a" you can write typeof a or typeof (a).
typeof operator is used when you need to get the data type of some variable to perform some task.
The typeof operator gives some unexpected results shown below so be careful when using it.
Example
var str = "food"; // String
var num = 10; // Number
var bool = true; // boolean
var undf; // undefined
var nl = null; // null
var obj = { "id": 121 }; // object
var symb = Symbol(); // symbol
var arr = ["mango", "banana", "orange"]; // array
var fxn = function () { }; // function
console.log(typeof str); // output: String
console.log(typeof num); // output: Number
console.log(typeof bool); // output: boolean
console.log(typeof undf); // output: undefined
console.log(typeof nl); // output: object
console.log(typeof obj); // output: Object
console.log(typeof symb); // output: Symbol
console.log(typeof arr); // output: Object
console.log(typeof fxn); // output: function
// Some other direct values
console.log(typeof 10); // output: Number
console.log(typeof Math.PI); // output: Number
console.log(typeof Infinity); // output: Number
console.log(typeof NaN); // output: number
console.log(typeof undefined); // output: undefinedConclusion
In this tutorial, we have learned about data types in javascript. We have also seen primitive data types like string, number, boolean, etc, and non-primitive data types like an object, array, function, symbol, etc.
